Derived Quantities »
In this node, you may define derived quantities that are calculated as a function of the compounds, pseudo-compounds and/or previously defined derived quantities. The definition of the derived quantities is similar to the pseudo-compounds, but derived quantities do not affect the reaction rates.
When doing parameter estimation, the derived quantities may also be reconciled, if you have experimental data available for them.
Grid ViewsWhen doing parameter estimation, the derived quantities may also be reconciled, if you have experimental data available for them.
Actions
Grid Views
Derived Quantities Definition
Terms in Derived Quantities Name
Derived Quantities Definition
This grid contains the list of Derived-Quantities and a Preview Pane for the selected one.
You may add or edit the name, defining equation type and constant term for each derived quantity. The grid columns are organized as follows:
Deleting a Derived Quantity
Top of Topic This grid contains the list of Derived-Quantities and a Preview Pane for the selected one.
You may add or edit the name, defining equation type and constant term for each derived quantity. The grid columns are organized as follows:
- The Derived Quantity column is used to enter the Derived Quantity name. It can be renamed by editing this field.
- The Type column is to select what type of equation will be used to calculate the derived quantity.
Two options are available, and the general expression for each of them are:
- Linear Sum:
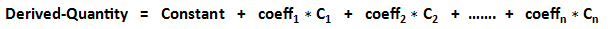
- Nonlinear Product:
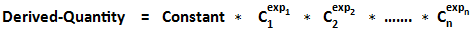
- Linear Sum:
- The Constant Term column is to enter the constant for both types, Linear Sum and Nonlinear Product. The default value is 0.
- The Expression column (Read-Only) displays derived quantity formula.
- The optional Units column is a text field (maximum 50 characters) used to define units for each Derived Quantity. The units defined here are shown in other nodes where the Derived Quantities are displayed.
- The Notes column (Optional) is a text field (maximum 100 characters) used to store comments about the derived quantities.
- In the last row, enter the name of the derived quantity. The row will change to edit mode, and you may save this new derived quantity with the <ENTER> key or clicking on the pencil icon in the row header.
Deleting a Derived Quantity
- Select the derived quantity row and use the <DELETE> key.
Terms in Derived Quantities Name
Here, the terms that define each derived quantity are entered. The columns are organized as follows:
- In the Compound column, you may enter a compound, a pseudo-compound, or a previously defined derived quantity for the corresponding term in the same row. You may enter up to ten(10) compounds/pseudo-compounds/derived quantities when defining a given derived quantity
- The Value column shows whether the total moles or the phase concentration is to be used for the derived quantity calculation. The options are as follows:
- When a real compound or a conserved pseudo-compound is selected in the compound column, the options in this column depend on the Concentration option selected in Units Configuration node:
When Molarity is selected, the options are Total Moles and Phase Name Molarity for liquid or gas phase, and Phase Name Moles for solid phase.
When Partial Pressure is selected, the options are Total Moles, Phase Name Molarity for liquid phase, Phase Name Partial Pressure for gas phase and Phase Name Moles for solid phase.
When Mass Density is selected, the options are Total Mass, Phase Name Mass Density for liquid or gas phase, and Phase Name Mass for solid phase.
- When a previously defined derived quantity or a non-conserved pseudo-compound has been selected in the compound column, this column is not applicable (N/A), since the derived quantity/pseudo-compounds are not specific to the phases.
- The Coefficient/Exponent column is used to enter the coefficient for the term (for a Linear Sum type equation), or the term exponent (for a Nonlinear Product type equation).
- When a real compound or a conserved pseudo-compound is selected in the compound column, the options in this column depend on the Concentration option selected in Units Configuration node:
Actions
Delete
Quick Run
Open Solver
Top of Topic
See Also: